Safety
Process Safety and Disaster Prevention
Targeting Zero Process Accidents
Placing the top priority for management on safety, we have established the Basic Policy on Safety.
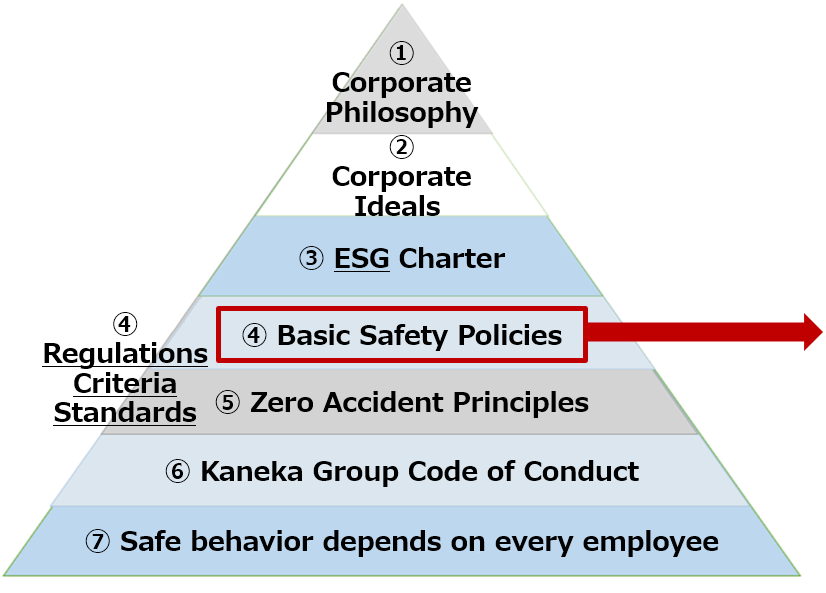
Basic Safety Policies
- Safety forms our management foundation, and is the basis of all corporate activities.
We take action with priority given to ensuring safety in all activities in the company. - Safety is the foundation of local and worldwide communities’ confidence in Kaneka.
We do our best to develop their trust. - Safety is based on our belief that “All accidents can be prevented.”
We always move forward without being satisfied with lukewarm results. - Safety is the responsibility of every employee in accordance with his/her duties.
We fulfill our responsibilities by mutually clarifying the duties we have assumed. - Safety must be maintained continuously.
We ensure safety through steady efforts on a daily basis.
Measures to Prevent Leakage Accidents
To prevent leakage from storage tanks, we continue to make improvements from the perspective of multiple layers of protection through risk assessments of all chemical storage facilities, in accordance with the KGSS (*1) process safety implementation standards on the storage and handling of chemical substances.
*1 KGSS (Kaneka Global Safety Standards)
A set of global safety standards shared across the Kaneka Group, both in Japan and internationally with the aim of ensuring onsite safety and security. We have put in place implementation standards (17 for occupational safety, 7 for process safety, and 1 for emergency response) under the respective management standards for occupational safety, process safety, and emergency response. A major feature of our approach is that each year we carry out gap assessments (of gaps between standards and actual conditions), and fill any gaps with the standards.
Plant Safety Initiatives
Emergency Response Training
Every year, all parent manufacturing sites hold comprehensive disaster drills that simulate emergencies such as major earthquakes, leaks of high-pressure gases or hazardous materials, and fires. These drills cover initial response measures, including in-house firefighting to contain damage, and are carried out in cooperation with local authorities and nearby industrial complexes.
Emergency Response and Evacuation Drills (Examples in fiscal 2023)
| № | Training | Content (Purpose) |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | Undisclosed scenario training | Abnormal events and scenarios are not disclosed in advance. A third party introduces ad-lib elements to train training participants in making on-the-spot judgments and communication methods. |
| (2) | Comprehensive disaster drills | Assuming plant damage, the entire plant participates in these drills, with participation by government representatives. Serves also to convey safety and security to the government. |
| (3) | Drills for nighttime power outages | Training to carry out bare minimum activities in complete darkness (while wearing a headlamp, etc.). |
| (4) | Toxic gas leakage evacuation drills | Evacuation drills positing a chlorine gas leak, including at adjacent plants. Includes evacuating buildings, wearing a gas mask, and practicing gas concentration measurement. |
Comprehensive Disaster Drills
| Manufacturing Site | Date | Participants | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Takasago Manufacturing Site | December 18, 2023 | 2,120 | An earthquake resulting in a fire caused by hazardous material leakage |
| Osaka Manufacturing Site | November 8, 2023 | 1,100 | An earthquake resulting in a fire caused by hazardous material leakage |
| Shiga Manufacturing Site | November 26, 2023 | 367 | An earthquake resulting in a fire |
| Kashima Manufacturing Site | December 12, 2023 | 72 | Hazardous material leakage and fire at the time of loading onto tanker trucks |
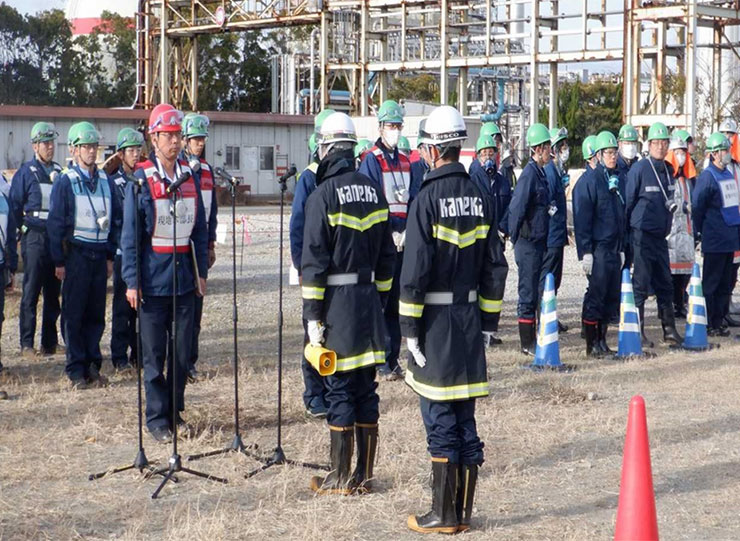
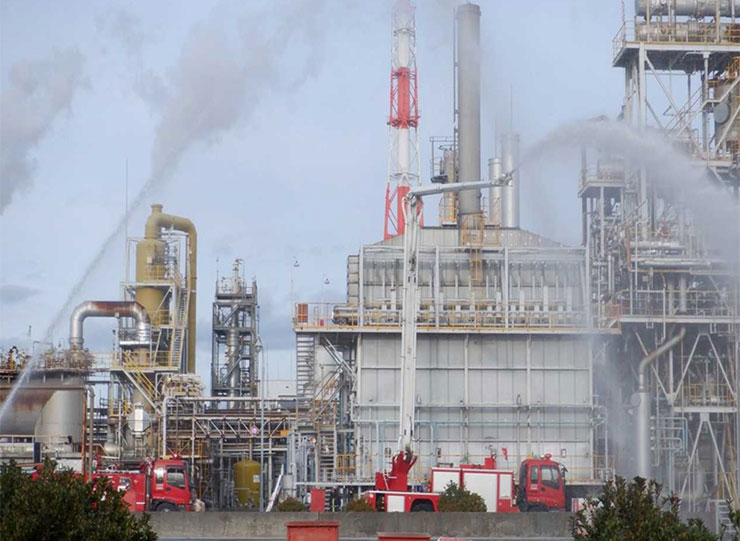
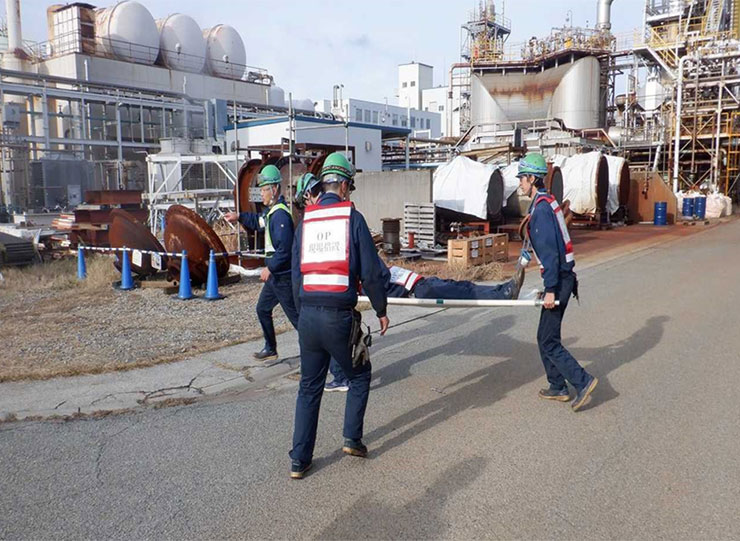



We advance countermeasures against natural disasters in order of priority, including promoting the earthquake-proofing of equipment in preparation for large-scale earthquakes, and implementing risk assessment for typhoons, heavy rains and floods, which have frequently occurred in recent years, based on hazard maps for all parent manufacturing sites and Group companies in Japan.
We also learn how to initially respond to a fire and how to use a hydrant to prevent the spread of a fire through daily training to ensure that we can immediately perform self-defense fire-fighting operations. To constantly improve our disaster coping skills and strengthen anti-disaster activities, we join a hydrant operation competition held locally, ranking higher every year.
Implementation of Safety Training
At Kaneka, we conduct various safety management and safety technology training sessions for newly appointed manufacturing managers, section chiefs, and dedicated safety engineers.
We evaluate the safety of our facilities using HAZOP (*2). The evaluation is mandated to be conducted by individuals registered as evaluators under our internal certification system. We also conduct HAZOP training annually to develop evaluators.
We are continuously working to enhance safety technologies by establishing methods for assessing the risks of chemical interactions and evaluating thermal runaway in reactions, thereby ensuring plant safety.
Learn more about our safety training details and achievements here.
*2HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Studies): A safety assessment method for identifying hazards in processes and operations. This systems engineering approach was originally developed for chemical plants.
CHECK & ACT
To reduce the number of process accidents, we will work to ensure risk assessment and intrinsic safety by setting risk assessment standards and fostering safety evaluators. We will continue to make company-wide efforts to thoroughly prevent recurrence and similar accidents.